Have you ever wondered how much of our global energy actually comes from coal? It’s a substantial amount, and understanding its role is critical for shaping our energy future. This article explores the global energy consumption powered by coal, providing a detailed look at its usage, impacts, and what the future might hold. From powering industries to heating homes, coal's presence is undeniable, influencing economies, environments, and energy policies worldwide. Let's delve into the specifics to understand its true scope.
All About Global Coal Energy Consumption
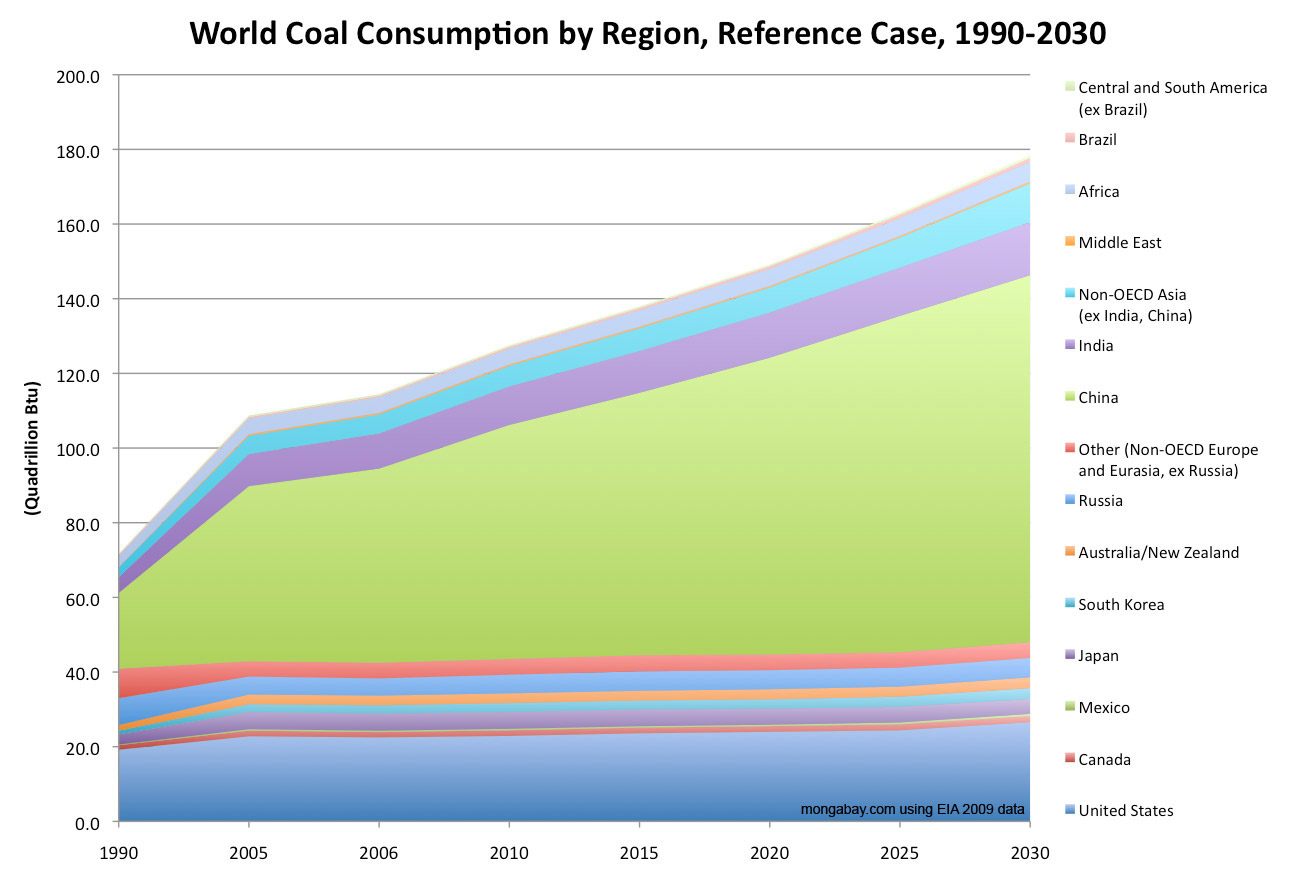
The question "How much energy from coal is used globally?" doesn't have a simple answer, as the numbers fluctuate based on economic activity, energy policies, and the adoption of alternative energy sources. However, we can say that coal remains asignificant player in the global energy mix, particularly in electricity generation and industrial processes. In recent years, while there's been a push towards cleaner energy, coal still accounts for a substantial percentage of worldwide power production and industrial heat. The exact figures are reported annually by organizations like the International Energy Agency (IEA) and the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), showing regional variations and trends. Understandingglobal coal usageis paramount to assessing its impact on climate change and planning for a sustainable energy future.
Historical Background and Key Developments
Coal's dominance didn't happen overnight. Its rise to prominence began during the Industrial Revolution. The readily available and relatively inexpensive fuel source fueled the steam engines that drove factories and railways, transforming economies and societies.Coal-fired power plantsemerged in the late 19th century, providing electricity to burgeoning cities. In the 20th century, coal's usage expanded further to include steel production and other industrial processes. However, the environmental consequences of burning coal, including air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions, gradually became apparent, leading to increased regulation and a search for cleaner alternatives. The development ofclean coal technologies, such as carbon capture and storage, represents an ongoing effort to mitigate the environmental impact of coal usage.
Unique Features of Coal Energy
Despite its environmental drawbacks, coal possesses certain characteristics that contribute to its continued usage. One key factor is its abundance and wide geographic distribution. Unlike oil and natural gas, which are concentrated in certain regions, coal reserves are found in many countries, making it a more accessible and secure energy source for some nations. Secondly, existing coal-fired power plants represent a significant infrastructure investment. Replacing these plants with renewable energy sources requires substantial capital and planning. This inertia, combined with the relatively low cost of coal in some markets, makes it difficult to quickly transition away from coal. Furthermore, coal provides a baseload power source, meaning it can reliably generate electricity around the clock, unlike some renewable sources that are intermittent. Theseunique characteristicsof coal are critical factors in shaping its continued relevance in the global energy mix.
Expert Opinions and Testimonials
While transitioning away from coal is widely seen as essential for addressing climate change, many experts acknowledge the challenges involved. Some argue that a phased approach is necessary, allowing time for the development and deployment of alternative energy technologies and the retraining of workers in affected industries. Others advocate for investing incarbon capture technologiesto reduce emissions from existing coal-fired plants. Expert opinions highlight the complexity of the situation, emphasizing the need for a balanced approach that considers both environmental and economic factors. Testimonials from industry representatives often stress the importance of ensuring a reliable and affordable energy supply, while environmental advocates call for a rapid transition to renewable energy.
Benefits of Global Coal Energy Consumption for Users
Even with increasing emphasis on sustainable energy, there are reasons coal remains in use. Coal power plants offer a relativelyconsistent energy supply, which is essential for modern life, providing stable electricity to homes, businesses, and industries. While not directly benefitting individual users, it stabilizes the grid. The economic benefits associated with coal are also a draw. In regions with abundant coal reserves, it represents a local resource that reduces dependence on foreign energy sources, thus strengthening energy security.
Real-Life Examples of Benefits
Consider a manufacturing plant relying on acoal-fired power plantfor its electricity. The consistent and affordable energy allows the plant to operate at full capacity, contributing to economic growth and job creation. Or imagine a cold winter in a region where coal is used for heating. While perhaps less efficient than other methods, it may be a vital source of warmth. These real-life examples demonstrate the ongoing importance of coal in providing energy to various sectors of society, even as efforts to transition to cleaner alternatives intensify.
Comparing Coal with Alternative Technologies
While coal offers advantages in terms of cost and reliability in some contexts, it falls short compared to alternative technologies in terms of environmental impact. Renewable energy sources like solar and wind generate electricity with minimal greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution. Natural gas, while still a fossil fuel, produces less carbon dioxide per unit of energy than coal.Nuclear poweroffers a carbon-free baseload power source, but faces challenges related to waste disposal and safety concerns. The choice of energy source involves a complex trade-off between cost, reliability, and environmental impact.
Data and Research Findings
Data consistently show that coal is the most carbon-intensive fossil fuel. Research from organizations like the IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change) demonstrates the urgent need to reduce coal consumption to mitigate climate change. The EIA projects future energy demand and supply, taking into account factors such as economic growth, technological advancements, and energy policies. These data and research findings provide a valuable evidence base for policymakers and energy planners to make informed decisions about the future of coal and other energy sources.
How to Understand and Track Global Coal Usage
While you won't beusingglobal coal usage in the same way you'd use a product, understanding it is essential. Here are some ways to do so:
1. Consult Reputable Sources
The first step in understanding global coal usage is to consult reputable sources of information. The IEA and the EIA are excellent sources, providing comprehensive data, analysis, and projections on global energy markets. Look for reports oncoal production, consumption, and trade, as well as analyses of trends and factors influencing coal usage.
2. Track Regional Trends
Global coal usage is not uniform. It varies significantly across regions, with some countries heavily reliant on coal and others rapidly transitioning to cleaner energy sources. Tracking regional trends is crucial to understanding the overall picture. Pay attention to developments in countries like China and India, which are major coal consumers. Also monitor the progress of developed countries in phasing out coal and adopting renewable energy.
3. Analyze Policy Changes
Energy policies play a significant role in shaping coal usage. Government regulations, incentives, and carbon pricing mechanisms can influence the demand for coal and the investment in coal-fired power plants. Analyze policy changes at the national and international levels to understand their potential impact on global coal usage.
Tips Before Evaluating Information on Coal Energy
Before diving into data about coal energy, consider these tips: Source Credibility: Always verify the credibility of the source. Date of Information: Energy data can change quickly, so review the date of the information. Context is Key:Understand the context behind data and claims.
Common Issues and Solutions Related to Understanding Coal Usage Data
One common challenge is thecomplexity of energy data. Statistical reports can be difficult to interpret, and different sources may use different methodologies or definitions. To overcome this, take the time to understand the data definitions and methodologies used by each source.
Another issue is thepotential for bias. Some organizations may have a vested interest in promoting or discouraging coal usage. Be aware of potential biases and consider multiple perspectives. Look for independent sources of information and cross-check data from different sources.
Conclusion
Understanding how much energy from coal is used globally is crucial for navigating the complex challenges of climate change and energy security. By consulting reputable sources, tracking regional trends, and analyzing policy changes, we can gain a deeper understanding of coal's role in the global energy mix and its potential impact on the environment. As the world transitions to cleaner energy sources, it is essential to continue monitoring coal usage and working towards a more sustainable energy future.