Ever wondered how much power is packed into that lump of coal? The energy content of coal varies considerably based on its type and grade, impacting everything from power plant efficiency to environmental impact. Understanding these differences is crucial for making informed decisions about energy production and usage. This article delves into the fascinating world of coal energy, exploring how different types of coal contain varying amounts of energy, ultimately affecting their suitability for different applications.
All About How Much Energy Is in Coal by Type and Grade?
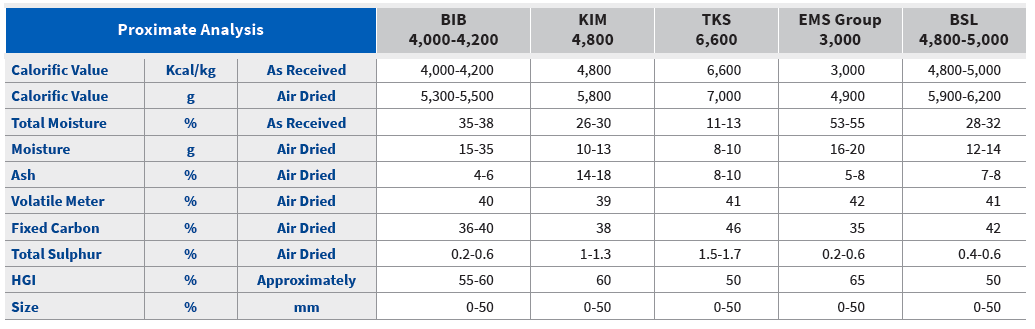
The amount of energy stored within coal, typically measured in British Thermal Units per pound (BTU/lb) or megajoules per kilogram (MJ/kg), is a critical factor determining its value as a fuel source. This energy content, also known as itsheating value, is directly related to the coal's rank, which is determined by its carbon content, volatile matter, moisture content, and ash content. Higher-rank coals generally have a higher heating value, meaning they release more energy when burned. Coal's energy density plays a significant role in the global energy market, affecting everything from power generation to steel production. Different ranks of coal exist because of the varying pressures and temperatures the material is exposed to over geological time. Peat is an early form of coal, while anthracite is a very hard, black, high-carbon coal.
Coal’s story began millions of years ago with the accumulation of plant matter in swampy environments. Over time, this organic material was buried under layers of sediment, subjected to immense pressure and heat. This process, known ascoalification, gradually transformed the plant matter into the various ranks of coal we know today. The process of coal formation is ongoing, however, it takes thousands or millions of years.
What differentiates coal from other solutions is its relatively high energy density compared to other fossil fuels, at least compared on a volume basis. It's also abundant and relatively inexpensive in many parts of the world, though this advantage is increasingly offset by environmental concerns. The convenience of coal as a source of fuel is something that made it a main source of fuel.
"Coal is a foundational energy source, and understanding its different types is crucial for optimizing its use while mitigating its environmental footprint," says Dr. Emily Carter, a renowned energy researcher at Princeton University. Her work emphasizes the importance of moving towards cleaner coal technologies.
Benefits of How Much Energy Is in Coal by Type and Grade? for Users
Understanding the energy content of different coal types directly impacts the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of power generation. Power plants can optimize their fuel selection based on the specific energy needs and environmental regulations, leading to more efficient energy production. For example, using higher-rank coal with a higher heating value can reduce the amount of fuel needed to generate a given amount of electricity, thereby lowering fuel costs and reducing emissions.
Consider a power plant that switches from using sub-bituminous coal to bituminous coal. The higher energy content of the bituminous coal means that the plant needs to burn less coal to generate the same amount of electricity. This results in lower fuel costs, reduced emissions, and potentially lower maintenance costs due to less ash and other byproducts. This is often the driving factor when deciding on the type of coal to use.
Compared to natural gas or oil, coal generally has a lower energy content per unit mass, but it's often cheaper and more readily available. However, technologies for producing syngas, coal gasification, or producing liquid fuels like diesel, methanol or gasoline from coal exist, but their long-term benefits may be questionable. Renewable energy sources like solar and wind offer cleaner alternatives, but they are intermittent and require energy storage solutions to ensure a reliable power supply. Coal and nuclear energy both have very high energy densities.
Research from the International Energy Agency (IEA) demonstrates that optimizing coal selection based on energy content and emissions characteristics can significantly improve the overall efficiency of coal-fired power plants. Data shows that the use of high-efficiency, low-emissions (HELE) coal technologies can reduce CO2 emissions by up to 30% compared to traditional coal-fired power plants.
How to Use How Much Energy Is in Coal by Type and Grade?
Here's a simplified guide on how to understand and utilize the energy content information of different coal types:
1. Identify the Coal Type
The first step is to determine the type or rank of coal you are dealing with. Common types include anthracite, bituminous, sub-bituminous, and lignite. This information is usually provided by the coal supplier or can be determined through laboratory analysis. You should be able to acquire the coal type from a lab if necessary.
Best Practice: Always request a detailed coal analysis report from your supplier. This report should include information on the coal's rank, heating value, moisture content, ash content, and sulfur content.
2. Determine the Heating Value
Once you know the coal type, you need to find its heating value, typically expressed in BTU/lb or MJ/kg. This information can be found in the coal analysis report or through online resources that provide typical heating values for different coal types. The BTU or MJ values can change depending on the grade and region of coal, but they should be roughly similar.
Common Mistake to Avoid: Relying on generic heating values without considering the specific characteristics of the coal you are using. Always use the heating value from a recent and accurate coal analysis report.
3. Calculate the Energy Output
With the coal type and heating value known, you can calculate the total energy output for a given amount of coal. For example, if you have 1000 lbs of bituminous coal with a heating value of 13,000 BTU/lb, the total energy output would be 13,000,000 BTU. Be sure to include the correct units for the mass and energy when calculating.
Ensure Each Step is Easy to Follow: Use consistent units and double-check your calculations. Consider using online calculators or spreadsheet software to automate the process and reduce the risk of errors.
Tips Before Using How Much Energy Is in Coal by Type and Grade?
Before using coal based on its energy content, consider these points: Preparation Guidelines: Ensure you have a complete understanding of the coal's characteristics, including its moisture content, ash content, and sulfur content. These factors can affect the overall efficiency and environmental impact of coal combustion. Be aware of the type of coal and the effects it has, as coal types such as anthracite may have more heavy metals. Recommendations: Avoid using coal with high sulfur content, as this can lead to acid rain and other environmental problems. Instead, opt for low-sulfur coal or implement sulfur dioxide (SO2) emission control technologies. Consequences of Ignoring these Tips: Ignoring these tips can result in lower energy efficiency, increased emissions, and potential damage to combustion equipment. It can also lead to regulatory fines and penalties for violating environmental regulations.
Common Issues and Solutions Related to How Much Energy Is in Coal by Type and Grade?
Users may face issues related to inconsistent heating values or unexpected emissions.
Problem: Inconsistent heating values can lead to inefficient combustion and difficulty in maintaining a stable energy output. Solution: Regularly test coal samples to ensure consistent quality and heating value. Implement quality control measures at the coal supply source to minimize variations. Problem: Unexpected emissions, such as sulfur dioxide (SO2) or nitrogen oxides (NOx), can exceed regulatory limits and cause environmental problems. Solution: Use emission control technologies, such as scrubbers or selective catalytic reduction (SCR), to reduce emissions. Also, consider switching to lower-sulfur coal or using alternative fuels.
Conclusion
Understanding the energy content of coal, based on its type and grade, is essential for efficient energy production, environmental protection, and cost optimization. By understanding the different types of coal, the user can optimize the energy usage and reduce the amount of greenhouse gases emitted. Coal isn't going away anytime soon, but it is worth finding more sustainable means.
Remember to consider the coal's characteristics, including its heating value, moisture content, ash content, and sulfur content, when making decisions about coal usage. Consider the energy densities as you make the decision on which fuel to use. Implementing the tips and solutions provided in this article can help you maximize the benefits of coal while minimizing its environmental impact. By making informed choices about coal usage, you can contribute to a more sustainable and energy-efficient future. As technology advances, there will be more sustainable options, and hopefully coal can be phased out.