Are you curious about how the electricity that powers our homes and businesses is generated? Coal plays a significant role, and understanding its journey from the earth to the power grid is essential. Let's explore how coal energy is produced in the US, focusing on the entire process from mining to electricity generation. This article will delve into the techniques, environmental considerations, and technologies involved in harnessing this important energy source, providing a comprehensive look at coal's contribution to the nation's power supply.
All About How Coal Energy Is Produced in the US
Coal energy production in the US is a multi-stage process that begins withcoal mining, followed byprocessing and transportation, and culminates inelectricity generationat power plants. Essentially, coal is a combustible sedimentary rock containing high amounts of carbon and hydrocarbons. When it is burned, it releases heat, which is then used to boil water, create steam, and drive turbines that generate electricity. Its significance in the US energy sector is considerable, historically providing a substantial portion of the nation's electricity.
Historical Context and Development
The use of coal as an energy source dates back centuries, but its large-scale adoption in the US began during the Industrial Revolution. Initially, coal fueled steam engines and heating systems. As technology advanced,coal-fired power plantsemerged, becoming a cornerstone of the electrical grid. Over time, mining techniques evolved from manual labor to highly mechanized operations. Similarly, power generation technology improved, with newer plants incorporating systems to increase efficiency and reduce emissions. The development ofclean coal technologiesaims to mitigate environmental impacts, although their effectiveness remains a subject of debate.
Unique Features of Coal Energy Production
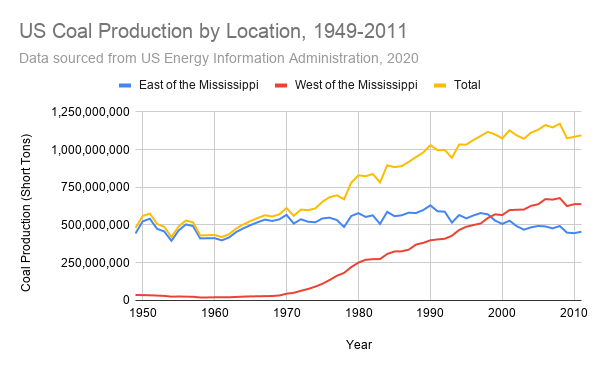
One distinct feature of coal energy production is its reliance onsubstantial infrastructurefor mining, processing, and transportation. Coal deposits are often located in remote areas, requiring extensive transportation networks, such as railways and barges, to move the coal to power plants. Another unique aspect is the variety of coal types, ranging from lignite (the lowest grade) to anthracite (the highest grade), each with different energy content and properties. This necessitates tailored mining and combustion techniques. Moreover, coal energy production faces increasing scrutiny due to its environmental impact, leading to ongoing research and development of cleaner alternatives and technologies.
Expert Perspectives on Coal Energy
Experts in the energy sector offer varying perspectives on the future of coal. Some argue that coal remains anessential fuel sourcedue to its abundance and relative affordability, advocating for continued investment inclean coal technologiesto minimize its environmental footprint. Others contend that the long-term viability of coal is uncertain, given the growing availability and decreasing cost of renewable energy sources like solar and wind. There's a broad agreement that coal's role in the energy mix will likely evolve as the US transitions to a more sustainable energy future.
Benefits of How Coal Energy Is Produced in the US for Users
The benefits of coal energy are primarily related to its role in providing a reliable and affordable source of electricity. For consumers, this translates tostable energy pricesand a consistent power supply. Coal-fired power plants can operate continuously, unlike some renewable sources that are intermittent. This reliability is especially important for industrial processes and critical infrastructure that require uninterrupted power.
Real-World Examples of Coal's Benefits
Consider a manufacturing plant that relies on a constant supply of electricity to operate its machinery. Coal-fired power can provide that stable energy source, ensuring continuous production. Similarly, hospitals, data centers, and other critical facilities often depend on coal-generated electricity to maintain essential services. These examples demonstrate the tangible benefits of coal energy in supporting key sectors of the economy and society.
Coal vs. Alternative Technologies
Compared to some renewable energy sources, coal offers the advantage ofdispatchability, meaning that power plants can adjust their output to meet demand fluctuations. Solar and wind energy, while environmentally friendly, are dependent on weather conditions and require energy storage solutions to ensure a consistent power supply. Nuclear power also provides baseload electricity but faces concerns related to safety and waste disposal. Each energy source has its own set of benefits and challenges, and the optimal mix depends on various factors, including cost, environmental impact, and reliability.
Data and Research on Coal's Impact
Studies on coal energy production reveal its significant economic impact, particularly in coal-producing regions. These regions often depend on the coal industry for employment and economic activity. However, research also highlights the environmental costs of coal, including air and water pollution, as well as greenhouse gas emissions. Balancing the economic benefits with the environmental impacts is a key challenge in shaping energy policy and promoting sustainable practices.
How to Use How Coal Energy Is Produced in the US
While "using" coal energy directly isn't something an individual consumer does, understanding the process can inform choices about energy consumption and support informed decision-making regarding energy policy. The process involves the following steps:
1. Mining Coal
Coal is extracted from the earth using various techniques, primarilysurface miningandunderground mining. Surface mining involves removing the overlying soil and rock to access coal seams near the surface, while underground mining involves digging tunnels to reach deeper coal deposits. The choice of mining method depends on the depth and location of the coal seam. Best practices include implementing safety protocols to protect miners and mitigating environmental impacts through reclamation efforts.
2. Processing and Cleaning Coal
After mining, coal undergoes processing to remove impurities and improve its energy content. This often involvescrushing, washing, and dryingthe coal. The goal is to remove dirt, rocks, and other unwanted materials that can reduce efficiency and increase emissions when the coal is burned. Common mistakes to avoid include neglecting proper dust control, which can lead to air pollution, and failing to manage water resources effectively during the washing process.
3. Burning Coal for Electricity
The processed coal is transported to power plants, where it is burned in largeboilersto generate heat. This heat is used to boil water, creating steam that drives turbines connected to generators. The generators convert the mechanical energy of the turbines into electrical energy, which is then transmitted through power lines to homes and businesses. Modern coal-fired power plants employ advanced technologies, such asscrubbersandcarbon capture systems, to reduce emissions and improve efficiency.
Tips Before Using How Coal Energy Is Produced in the US
Before considering coal energy, it's important to understand the broader implications of its use. This involves evaluating the environmental impacts, exploring alternative energy sources, and making informed decisions about energy consumption.
Environmental Impact Awareness
Coal combustion releases pollutants, includingsulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter, which can contribute to air pollution and respiratory problems. Additionally, coal is a significant source of greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to climate change. Before advocating for or supporting coal energy production, it's essential to understand these environmental costs and weigh them against the benefits.
Exploring Alternative Energy Sources
The US has abundant renewable energy resources, including solar, wind, geothermal, and hydropower. These sources offer cleaner alternatives to coal and can contribute to a more sustainable energy future. By supporting policies that promote the development and deployment of renewable energy technologies, individuals and communities can reduce their reliance on coal and mitigate its environmental impact.
Informed Energy Consumption
Making conscious choices about energy consumption can also help reduce the demand for coal-generated electricity. This includes conserving energy at home and in the workplace, using energy-efficient appliances and lighting, and supporting companies that prioritize sustainability. By reducing energy demand, we can collectively lessen the need for coal and other fossil fuels.
Common Issues and Solutions Related to How Coal Energy Is Produced in the US
Coal energy production is not without its challenges. Here are some common issues and potential solutions:
Air and Water Pollution
Burning coal releases pollutants that can harm air and water quality. Solutions include installingscrubbersin power plants to remove sulfur dioxide, usingselective catalytic reductionto reduce nitrogen oxides, and implementingwastewater treatment systemsto prevent water pollution.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Coal is a major source of greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to climate change. Solutions include transitioning tolower-carbon energy sources, such as natural gas and renewable energy, and developingcarbon capture and storagetechnologies to capture CO2 emissions from power plants and store them underground.
Mining Impacts
Coal mining can have significant environmental impacts, including habitat destruction, soil erosion, and water contamination. Solutions include implementingresponsible mining practices, such as restoring mined land and preventing water pollution, and supporting policies that protect sensitive ecosystems.
Conclusion
Coal energy production has played a significant role in powering the US economy and society for many years. However, its environmental impacts necessitate a careful evaluation of its role in the future energy mix. By understanding the benefits and challenges of coal energy, exploring alternative energy sources, and making informed choices about energy consumption, we can work towards a more sustainable and environmentally responsible energy future. Remember that even though individuals don't directly "use" coal, understanding the process empowers informed decisions about energy consumption and policy. Let's continue to learn and adapt as technology and societal priorities evolve, striving for an energy landscape that balances economic needs with environmental stewardship.