How Do We Use Coal for Energy Production?
Have you ever wondered how we power our homes and industries? A significant portion of the electricity we use comes from coal. Coal, a fossil fuel formed over millions of years, remains a crucial energy source globally. This post explores the intricate processes involved in using coal for energy production, detailing its historical significance, the various methods employed, and its ongoing role in the energy landscape. Understanding how we use coal for energy production is essential, especially when considering the environmental impact and alternative energy sources, making informed discussions about energy policy and future sustainability possible. From its extraction to its combustion, let's delve into the world of coal-fired power plants.
All About Coal for Energy Production
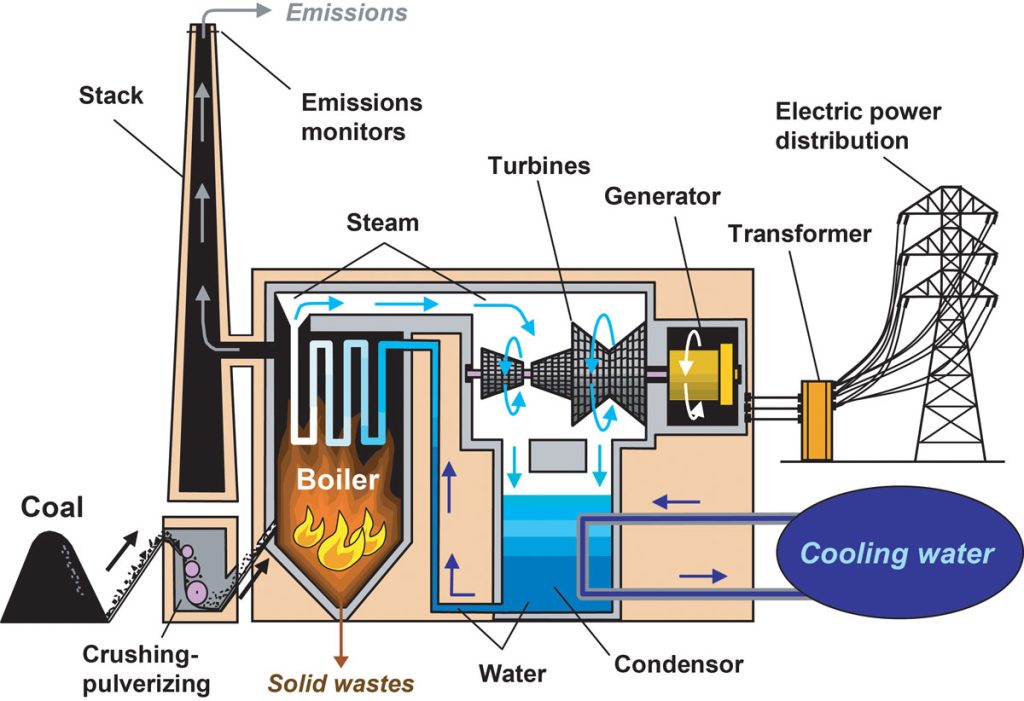
Coal for energy production involves a series of steps, transforming a solid fossil fuel into usable electricity. The process begins withcoal extraction, which can occur through surface mining or underground mining, depending on the depth and location of the coal seams. Once extracted, the coal undergoespreparation, which involves crushing, washing, and sorting to remove impurities and ensure a consistent size for efficient combustion. The cleaned coal is then transported to power plants, where the magic – or rather, the science – happens.
The significance of coal in technology lies in itshigh energy densityand its role inbaseload power generation. Baseload power refers to the consistent, reliable electricity supply that power plants provide, regardless of fluctuations in demand. Coal plants have traditionally been excellent at fulfilling this role. While renewable energy sources like solar and wind are becoming increasingly prominent, coal still provides a stable and readily available energy source for many regions.
Historically, coal has been a cornerstone of industrial revolutions. From powering steam engines in the 18th century to fueling the massive electricity grids of the 20th and 21st centuries, coal's abundance and relatively low cost have made it an attractive option. Key developments include advancements in combustion technologies, like pulverized coal combustion and fluidized bed combustion, which improve efficiency and reduce emissions.
What differentiates coal from other solutions is itsestablished infrastructure. The global network of coal mines, transportation systems, and power plants represents a significant investment and provides a ready-made system for energy generation. However, this advantage is increasingly offset by growing environmental concerns and the rise of more sustainable alternatives.
Expert opinions on coal usage vary widely. While some argue that coal is necessary for maintaining energy security and affordability, others emphasize the urgency of transitioning to cleaner energy sources to mitigate climate change. Testimonials from communities heavily reliant on coal-fired power plants often highlight the economic benefits, while those from areas affected by coal mining or pollution emphasize the environmental and health costs.
Benefits of Coal for Energy Production for Users
The primary benefit of coal for energy production for users isreliable and affordable electricity. For decades, coal-fired power plants have been a backbone of the electricity grid, providing a consistent power supply that keeps the lights on and powers industries. The relatively low cost of coal compared to some other fuels has translated to lower electricity prices for consumers in many regions.
Real-life examples of its benefits are abundant. In countries like India and China, coal remains a critical fuel source for meeting the rapidly growing energy demands of expanding economies. Even in developed nations, coal plants continue to play a role in ensuring a stable electricity supply, particularly during periods of high demand or when renewable energy sources are intermittent.
When comparing coal with alternative technologies, thecost-effectivenessandbaseload capacityof coal plants often stand out. While renewable energy sources like solar and wind have become increasingly competitive, they often require significant investments in energy storage or grid upgrades to ensure a reliable power supply. Nuclear power offers another baseload alternative, but faces concerns about safety and waste disposal.
Data and research findings consistently show that coal-fired power plants can provide a stable and affordable energy source. However, these benefits come at a significant environmental cost, including greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution. Therefore, the future of coal in energy production depends on finding ways to mitigate these negative impacts through technologies like carbon capture and storage, or transitioning to cleaner alternatives.
How to Use Coal for Energy Production
1. Coal Extraction and Preparation
The first step in using coal for energy production is, naturally,extracting the coalfrom the earth. This is a complex process that can involve either surface mining, where layers of soil and rock are removed to access shallow coal seams, or underground mining, where tunnels are dug deep into the earth to reach deeper coal deposits.
Best practices for coal extraction emphasizesafety and environmental responsibility. Miners must adhere to strict safety regulations to minimize the risk of accidents, and mining companies must implement measures to mitigate environmental impacts, such as land reclamation and water treatment.
2. Combustion and Steam Generation
Once the coal is extracted and prepared, it'sburned in a boilerto generate heat. This heat is used to boil water and produce high-pressure steam. The steam then drives a turbine, which is connected to a generator.
Common mistakes to avoid during combustion include incomplete burning, which can lead to increased emissions, and improper boiler maintenance, which can reduce efficiency and increase the risk of equipment failure.
3. Electricity Generation and Distribution
Therotating turbinespins the generator, which converts the mechanical energy into electrical energy. This electricity is then transmitted through power lines to homes and businesses.
Further steps include managing waste products, such as ash, and implementing pollution control technologies to reduce emissions.
Tips Before Using Coal for Energy Production
Before using coal for energy production, it's crucial to have acomprehensive environmental management planin place. This plan should address issues such as air and water pollution, land degradation, and greenhouse gas emissions.
Recommendations include investing inclean coal technologies, such as carbon capture and storage, and implementing strategies to reduce emissions from existing power plants.
Ignoring these tips can have significant consequences, including environmental damage, health problems for nearby communities, and increased regulatory scrutiny.
Common Issues and Solutions Related to Coal for Energy Production
Potential problems that users might face includehigh emissions, water pollution, andland degradation.
Practical solutions include implementingpollution control technologies, such as scrubbers and electrostatic precipitators, to reduce air pollution, and usingwater treatment systemsto clean wastewater before it is discharged. Land reclamation efforts can help to restore mined areas to their original condition.
Conclusion
Coal for energy production has been a cornerstone of industrial development for centuries, providing a reliable and affordable energy source. However, the environmental impacts of coal usage are undeniable, and the transition to cleaner energy sources is essential for a sustainable future. While coal may continue to play a role in the energy mix for some time, it's crucial to implement technologies and strategies to mitigate its negative impacts and explore alternative energy options. Final recommendations include investing in research and development of clean coal technologies, promoting energy efficiency, and supporting the growth of renewable energy sources. Understanding how we use coal for energy production empowers us to make informed decisions about our energy future and contribute to a more sustainable world. By embracing innovation and prioritizing environmental responsibility, we can ensure a cleaner, healthier, and more prosperous future for all.