How is energy generated from coal worldwide, and why does it remain such a significant, albeit controversial, part of the global energy landscape? Let’s dive into the process, its history, the pros and cons, and the future of coal-fired power generation. Coal power, crucial for electricity generation worldwide, involves burning coal to produce steam, which in turn drives turbines to create electricity. While essential, understanding the process and its impacts is key to navigating our energy future.
All About How Energy Is Generated from Coal Worldwide
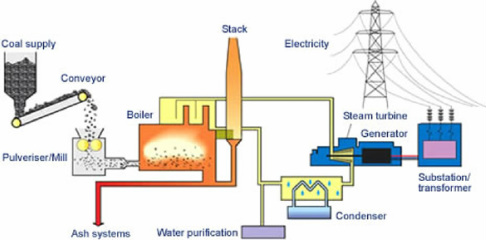
The burning of coal to generate electricity is a well-established process that has powered industries and homes for well over a century. But how does this process actually work? It all begins withcoal, a fossil fuel formed over millions of years from decayed plant matter. This coal is mined from the earth, transported to power plants, and then burned in large furnaces. The heat from this combustion boils water, creating high-pressuresteam. This steam is then directed at the blades of aturbine, causing it to spin. The turbine is connected to agenerator, which converts the mechanical energy of the spinning turbine into electrical energy. This electricity is then transmitted through power lines to homes, businesses, and industries. This entire process relies on the transformation of chemical energy (in the coal) to thermal energy (heat), then to mechanical energy (turbine spinning), and finally to electrical energy. The global reliance on coal power underscores its impact on energy security, yet also raises significant environmental concerns about carbon emissions and air quality.
The history of coal-fired power generation is intertwined with the Industrial Revolution. In the late 19th century, the invention of the steam engine and the development of the electrical grid spurred the demand for coal as a primary energy source. Early power plants were relatively inefficient and emitted significant amounts of pollution. Over time, however, technologies have evolved to improve efficiency and reduce emissions. For instance, supercritical and ultra-supercritical power plants operate at higher temperatures and pressures, resulting in greater energy conversion efficiency and lower carbon dioxide emissions per unit of electricity generated. Despite these advancements, the fundamental process of burning coal to create steam and drive turbines remains the core principle.
What sets coal-fired power generation apart from other energy sources, such as natural gas, nuclear, or renewables? One key difference is theavailability and affordabilityof coal in many regions. Coal reserves are abundant in countries like the United States, China, India, and Australia, making it a relatively inexpensive fuel source. This contributes to energy independence and security for these nations. Another difference lies in thereliabilityof coal-fired power plants. Unlike intermittent renewable sources like solar and wind, coal plants can operate continuously, providing a stable base load of electricity to the grid. However, the environmental impact of coal power, particularly its contribution to greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution, remains a significant drawback that differentiates it from cleaner alternatives.
Experts often point out the need for a balanced approach. "Coal isn't going away overnight," argues Dr. Emily Carter, a professor of Energy and Environmental Science. "Instead, we need to focus on developing and deploying carbon capture and storage technologies to mitigate its environmental impact while we transition to cleaner energy sources." Another expert, energy analyst John Davies, emphasizes the economic considerations: "For many developing nations, coal remains the most affordable and accessible energy source, which makes a rapid transition to renewables a significant challenge." These perspectives highlight the complex interplay of factors influencing the use of coal power worldwide.
Benefits of How Energy Is Generated from Coal Worldwide for Users
For end-users, the benefits of coal-fired power generation often manifest in the form ofaffordable and reliable electricity. When coal is readily available and cheap, electricity prices tend to be lower, benefiting both households and businesses. This affordability can be especially crucial for low-income households, where energy costs represent a significant portion of their budget. Additionally, the constant availability of power from coal-fired plants provides a sense of security, ensuring that lights stay on and essential appliances function reliably, regardless of weather conditions or time of day.
Consider a manufacturing plant that relies on a constant supply of electricity to operate its machinery. If the plant were to rely solely on intermittent renewable sources, it would be susceptible to disruptions during periods of low sunlight or wind. A coal-fired power plant, on the other hand, can provide a continuous and predictable supply of electricity, ensuring that the plant can maintain its production schedule without interruptions. In this case, coal power contributes to economic stability and job creation.
Comparing coal-fired power to other energy sources reveals some interesting trade-offs. While natural gas power plants offer lower carbon emissions compared to coal, they are often subject to fluctuating fuel prices, which can impact electricity rates. Nuclear power provides a clean and reliable source of electricity but involves high upfront costs and concerns about nuclear waste disposal. Renewable sources like solar and wind are environmentally friendly but are intermittent and require energy storage solutions to ensure continuous power supply. Data from the International Energy Agency (IEA) consistently shows that coal remains a dominant fuel source in many countries, particularly in Asia, due to its affordability and abundance. However, the IEA also emphasizes the urgent need to transition to cleaner energy sources to meet climate goals.
How to Generate Energy from Coal Worldwide
The generation of energy from coal involves several key steps, from coal extraction to electricity delivery. While the process may seem straightforward, optimizing each step can improve efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
1. Coal Extraction and Preparation
The first step involves extracting coal from the earth. This can be done throughsurface mining(also known as strip mining), where coal seams are close to the surface, or throughunderground mining, where coal seams are deep beneath the surface. Surface mining is generally more cost-effective but can have a greater environmental impact, while underground mining is more labor-intensive but can access deeper coal reserves. After extraction, the coal is typically processed to remove impurities like rock and ash, improving its energy content and reducing emissions when burned.
Best practices include implementing advanced mining techniques that minimize environmental damage and ensuring proper coal storage to prevent spontaneous combustion and runoff. Optimization tips include using computerized monitoring systems to track coal quality and optimize the blending process, ensuring a consistent fuel supply for the power plant.
2. Combustion and Steam Generation
The prepared coal is then transported to a power plant and fed into a large furnace, where it iscombustedat high temperatures. The heat from the combustion boils water in a boiler, producing high-pressure steam. The efficiency of this process depends on the design of the boiler and the quality of the coal.
Common mistakes to avoid include using outdated boiler technology that leads to inefficient heat transfer and failing to maintain optimal combustion conditions, which can result in incomplete burning and increased emissions. Regular maintenance and upgrades to boiler systems are crucial for maximizing efficiency and minimizing environmental impact.
3. Power Generation and Distribution
The high-pressure steam is then directed at the blades of aturbine, causing it to spin. The turbine is connected to agenerator, which converts the mechanical energy of the spinning turbine into electrical energy. The electricity is then transmitted through power lines to homes, businesses, and industries.
This process requires careful monitoring and control to ensure stable and reliable power generation. Common mistakes to avoid include neglecting regular maintenance of turbines and generators, which can lead to breakdowns and reduced efficiency, and failing to optimize grid management, which can result in power losses during transmission.
Tips Before Using Coal for Energy Generation
Before embarking on coal-fired power generation, careful preparation is essential to minimize environmental impact and maximize efficiency. Here are some key guidelines: Conduct thorough environmental impact assessments: Before building a coal-fired power plant, it's crucial to assess the potential environmental impacts, including air and water pollution, habitat destruction, and greenhouse gas emissions. This assessment should inform the design and operation of the plant to minimize these impacts. Invest in advanced emission control technologies: Coal-fired power plants can release harmful pollutants into the air, such as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter. Investing in technologies like scrubbers, selective catalytic reduction (SCR) systems, and electrostatic precipitators can significantly reduce these emissions. Implement carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies:CCS technologies capture carbon dioxide emissions from power plants and store them underground, preventing them from entering the atmosphere. While CCS is still in its early stages of development, it holds significant potential for reducing the carbon footprint of coal-fired power generation.
Ignoring these tips can have serious consequences, including environmental damage, public health risks, and regulatory penalties. Failing to implement emission control technologies can result in air pollution that harms human health and ecosystems. Neglecting environmental impact assessments can lead to unsustainable practices and long-term environmental damage.
Common Issues and Solutions Related to Coal Energy Generation
Despite its established technology, coal-fired power generation is not without its challenges. Here are some common issues and their solutions: Air pollution:Coal combustion releases harmful pollutants into the air, contributing to respiratory problems, acid rain, and other environmental issues.
Solution: Implement advanced emission control technologies like scrubbers, SCR systems, and electrostatic precipitators to reduce emissions. Water pollution: Coal mining and power plant operations can contaminate water sources with heavy metals and other pollutants.
Solution: Implement strict water management practices, including wastewater treatment and proper disposal of coal ash. Greenhouse gas emissions: Coal combustion is a major source of greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to climate change.
Solution: Invest in carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies and transition to cleaner energy sources. Coal ash disposal: Coal ash, a byproduct of coal combustion, can contain harmful pollutants and requires careful disposal.
Solution: Implement safe and sustainable coal ash disposal practices, such as using coal ash in construction materials or storing it in engineered landfills.
Conclusion
Generating energy from coal is a complex process with significant environmental and economic implications. While coal remains a crucial energy source for many countries, it's essential to mitigate its environmental impacts by implementing advanced emission control technologies, investing in carbon capture and storage, and transitioning to cleaner energy sources. By understanding the process, its benefits, and its challenges, we can make informed decisions about the future of coal power in a rapidly changing energy landscape. Moving forward, a balanced approach that considers both energy security and environmental sustainability will be crucial for ensuring a sustainable energy future for all.