How much of our electricity comes from coal these days? It's a question worth asking as we navigate the complexities of energy production and its impact on the environment. Coal has been a cornerstone of US energy for over a century, powering industries and homes, but its role is changing. Understanding coal's current contribution is crucial for grasping the evolving energy landscape and planning for a sustainable future. Let's delve into the details of coal's presence in the United States' energy mix today.
All About Coal's Role in US Energy Production
Defining exactlyhow muchof the US energy pie is coal-based requires looking at multiple facets of energy. While "energy" is a broad term encompassing all fuels used, electricity generation is where coal has historically played the largest role. It's not just about the percentage; it's about understandingwhythat percentage is what it is and what factors influence it. This includes the rise of natural gas, renewable energy sources, and changing environmental regulations.
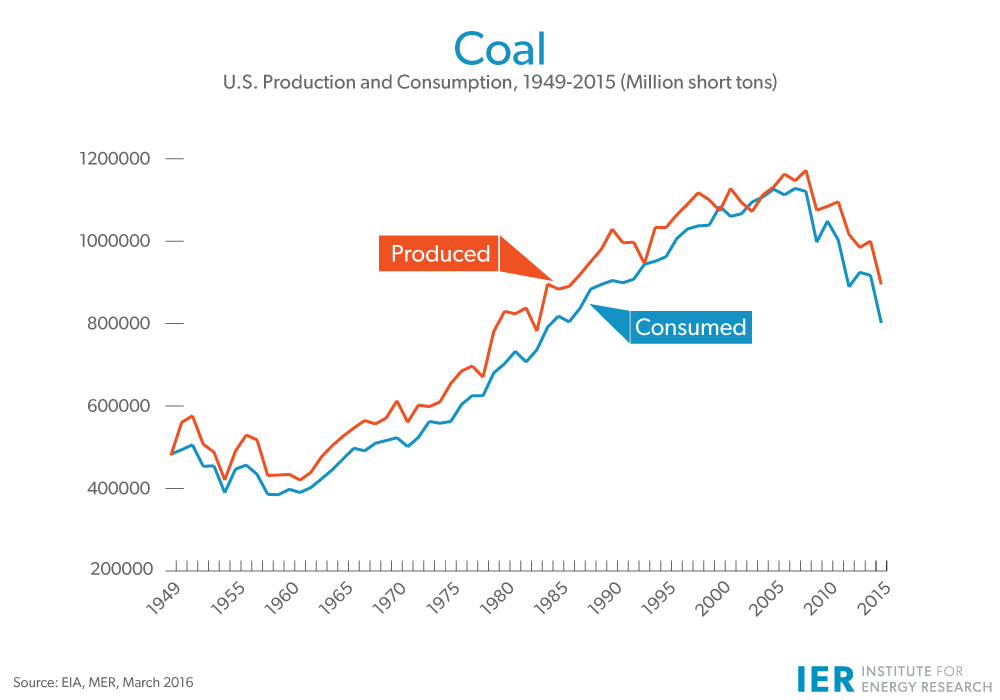
Historically, coal was king. The Industrial Revolution was fueled by coal, and the United States built its industrial might on the back of this abundant and relatively inexpensive resource. In the early 20th century, coal dominated electricity generation, providing the vast majority of power. The boom continued well into the latter half of the century.
However, the latter part of the 20th century and the beginning of the 21st century marked a shift. Stricter environmental regulations aimed at curbing air pollution, concerns about climate change, and the increasing competitiveness of other energy sources like natural gas and renewables began to erode coal's dominance. Technological advancements in hydraulic fracturing (fracking) dramatically increased the availability and affordability of natural gas, making it a strong contender for power generation. The growth of wind and solar power, driven by government incentives and decreasing costs, further diversified the energy mix.
Today, coal's share has declined significantly from its peak. While it remains a part of the picture, it’s no longer the dominant player. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), coal accounted for roughly16% of U.S. electricity generation in 2023. This figure fluctuates based on factors like seasonal demand, natural gas prices, and renewable energy output. This represents a dramatic shift from decades past, highlighting the impact of technological advancements and policy changes on energy production.
What differentiates coal from other solutions? Historically, it offered a reliable and readily available source of baseload power – electricity that can be consistently generated to meet continuous demand. Coal-fired power plants can operate 24/7, unlike some renewable sources like solar or wind, which are intermittent. However, modern grid technologies and energy storage solutions are increasingly addressing this intermittency, making renewables more viable. Furthermore, coal's high carbon emissions are a significant drawback compared to cleaner alternatives like natural gas, nuclear, and renewables.
Expert opinions highlight the complex trade-offs involved in energy policy. Some argue that coal still plays a crucial role in ensuring grid reliability, especially in regions with limited access to other energy sources. Others emphasize the urgent need to transition away from coal to mitigate climate change and improve public health. The future of coal in the US energy mix depends on technological advancements in carbon capture and storage, policy decisions regarding environmental regulations, and the continued growth of renewable energy sources.
Benefits of Alternative Energy Sources for Users
The move away from coal and towards alternative energy sources brings numerous benefits for consumers. These benefits extend beyond just environmental considerations, impacting the economy, public health, and energy security.
One of the most significant benefits is improved air quality. Coal-fired power plants release pollutants such as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter, which contribute to respiratory problems, heart disease, and other health issues. Switching to cleaner energy sources like natural gas, wind, and solar can significantly reduce these emissions, leading to healthier communities and lower healthcare costs.
Economically, the growth of the renewable energy sector is creating jobs and stimulating innovation. The solar and wind industries, in particular, are experiencing rapid growth, offering opportunities for skilled workers in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance. Furthermore, renewable energy projects can bring economic benefits to rural communities by providing new sources of income and investment.
Another key benefit is increased energy security. Relying on a diverse mix of energy sources reduces dependence on any single fuel, making the energy system more resilient to disruptions in supply or price fluctuations. Renewable energy sources like wind and solar are domestically available, reducing the need to import fuels from other countries.
Compared to coal, alternative energy sources offer a range of advantages. Natural gas emits less carbon dioxide than coal, making it a cleaner option for power generation. Wind and solar power produce no greenhouse gas emissions during operation, making them the most environmentally friendly choices. Nuclear power, while not renewable, offers a reliable source of baseload power with low carbon emissions.
Data from the EIA supports these claims. The agency's reports show a clear trend of declining coal consumption and increasing renewable energy generation. This shift is driven by a combination of market forces, technological advancements, and policy decisions. As the cost of renewable energy continues to decline and environmental regulations become stricter, the transition away from coal is likely to accelerate.
How to Reduce Reliance on Coal-Based Energy
While transitioning away from coal is a complex process, there are several steps individuals and communities can take to contribute to a cleaner energy future.
1. Energy Efficiency
The first and perhaps most impactful step is to reduce energy consumption. This can be achieved through simple measures like using energy-efficient appliances, installing better insulation, and switching to LED lighting. Smart thermostats can also help optimize energy usage by automatically adjusting temperature settings based on occupancy and weather conditions.
Best practices include conducting an energy audit to identify areas where energy is being wasted and implementing targeted improvements. Optimization tips include sealing air leaks around windows and doors, upgrading to high-efficiency heating and cooling systems, and using power strips to turn off electronics when they are not in use.
2. Supporting Renewable Energy
Another important step is to support the development and deployment of renewable energy sources. This can be done by advocating for policies that promote renewable energy, investing in renewable energy companies, or purchasing renewable energy certificates (RECs). RECs represent the environmental attributes of renewable energy generation and can be purchased to offset the carbon footprint of electricity consumption.
Common mistakes to avoid include relying solely on fossil fuels and not exploring alternative energy options. By actively supporting renewable energy, individuals and communities can help accelerate the transition to a cleaner energy future.
3. Promoting Sustainable Transportation
Transportation is another major source of carbon emissions. Promoting sustainable transportation options such as walking, cycling, and public transit can help reduce reliance on fossil fuels. Electric vehicles (EVs) are also becoming increasingly popular, offering a cleaner alternative to gasoline-powered cars.
Further steps include advocating for investments in public transit infrastructure, supporting policies that incentivize EV adoption, and choosing fuel-efficient vehicles. Investing in carbon offset programs that support renewable energy and reforestation projects is also an important action.
Tips Before Transitioning Away from Coal
Before fully embracing alternative energy options, it's crucial to understand a few key considerations.
Preparation guidelines include assessing your energy needs and identifying the most suitable renewable energy options for your home or business. Researching local incentives and rebates can also help reduce the upfront costs of installing renewable energy systems.
What to avoid? Don't invest in outdated or inefficient technologies. Ensure that any renewable energy system you install is properly sized and installed by qualified professionals.
Possible consequences of ignoring these tips include higher energy costs, reduced system performance, and potential safety hazards. Taking the time to do your research and plan carefully can ensure a smooth and successful transition to a cleaner energy future.
Common Issues and Solutions Related to Shifting Away From Coal
Transitioning away from coal can present challenges, but understanding common issues and their solutions is key to a successful transition.
One potential problem is the intermittency of renewable energy sources like wind and solar. Solutions include investing in energy storage technologies, such as batteries, and developing smart grids that can balance supply and demand.
Another challenge is the high upfront cost of installing renewable energy systems. Solutions include government incentives, financing options, and community solar programs.
A further issue is the potential job losses in the coal industry. Solutions include providing retraining and support for workers transitioning to new industries, investing in economic diversification, and creating new jobs in the renewable energy sector.
Conclusion
Coal's role in the U.S. energy mix has been significant, but its share is declining as cleaner alternatives become more competitive. Understanding the current state of coal-based energy, its benefits, and the steps individuals and communities can take to reduce reliance on coal is crucial for creating a sustainable energy future. By embracing energy efficiency, supporting renewable energy, and promoting sustainable transportation, we can all contribute to a cleaner, healthier, and more secure energy future.
Ultimately, the journey toward a cleaner energy future is a shared responsibility. By understanding the complexities of energy production and consumption, we can make informed choices and work together to build a sustainable energy system for generations to come.