Did you ever wonder how those giant power plants churning out electricity actuallydoit? A significant portion of our world's power comes from coal, a process involving several stages to convert the stored energy within those black rocks into the electricity that powers our homes and businesses. From mining the coal to the moment it lights up your lightbulb, understanding this process helps us appreciate the complexities and impacts of our energy sources. This article delves into the intricate process of how a coal power plant extracts energy from coal, transforming it into usable electricity, exploring the key stages, benefits, and challenges. Coal-fired power plants remain a crucial part of the energy landscape, so let's explore how they work, touching upon thermal energy, steam turbines, and the overall electricity generation process.
All About How Energy is Extracted from Coal in a Power Plant
The journey of converting coal into electricity is a fascinating blend of physics, engineering, and a bit of chemistry. At its heart, it's all about releasing the energy locked within the chemical bonds of coal through combustion and then harnessing that energy to turn a turbine, which ultimately generates electricity. The power plant acts as a giant, carefully orchestrated machine to facilitate this process.
The Basics of Coal-Fired Power Generation
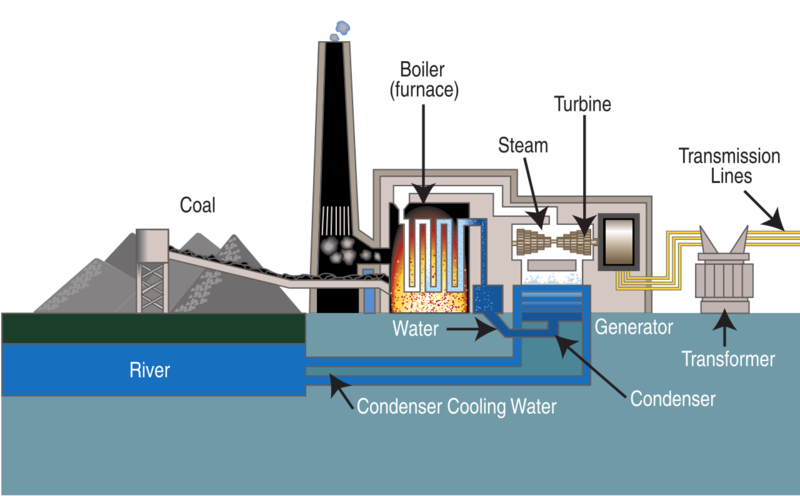
The core principle behind a coal power plant revolves around the principle ofthermodynamics:heat energy is used to create mechanical energy, which is then converted into electrical energy. Coal, a readily available and relatively inexpensive fuel source, is burned in a large furnace. This combustion process generates a tremendous amount of heat. That heat then boils water, creating high-pressure steam. This high-pressure steam is then directed to a turbine, causing it to spin rapidly. The spinning turbine is connected to a generator, which converts the mechanical energy into electrical energy. The electricity is then transmitted through power lines to homes and businesses. Essentially, a coal power plant is a sophisticated engine that converts the chemical energy in coal into electricity. Key steps includecombustion, steam generation, turbine operation, and electricity generation.
A Brief History of Coal Power
The use of coal for electricity generation dates back to the late 19th century with the invention of the steam turbine. As industrialization boomed, so did the need for efficient and reliable energy sources. Coal, being abundant and relatively easy to transport, quickly became the fuel of choice. Early power plants were relatively inefficient, but technological advancements over the decades have significantly improved efficiency and reduced environmental impact (though significant challenges remain). From the simple boilers of early industrial plants to the sophisticated supercritical and ultra-supercritical power plants of today, the history of coal power is one of continuous innovation and adaptation.Early adoption, industrial revolution, and technological advancementsare significant moments in the history of coal power.
What Makes Coal Power Unique?
Compared to other forms of power generation, coal power offers a few distinct advantages and disadvantages. One key advantage is itsreliability and base-load capability. Unlike renewable energy sources like solar and wind, coal plants can operate continuously, providing a stable and predictable supply of electricity. However, coal power also carries significant environmental concerns, including air pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and the impacts of coal mining. Compared to nuclear power, coal is more flexible in terms of fuel supply, but nuclear power offers significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions. Compared to natural gas, coal often has a lower fuel cost, but natural gas plants are typically quicker to build and operate more cleanly.
While concerns surrounding coal power are significant, some experts argue that coal, when coupled with carbon capture technologies, can still play a role in a diversified energy portfolio.Base-load capability and fuel accessibilityare unique features.
Benefits of Coal Power for Users
While the environmental impact of coal-fired power plants is a significant concern, it's also important to acknowledge the benefits it provides, particularly in terms ofenergy security and affordability.
Reliability and Stability
One of the most significant advantages of coal power is itsreliability. Coal-fired power plants can operate 24/7, providing a constant and dependable source of electricity. This is particularly important for maintaining grid stability and ensuring that power is available when needed, even during peak demand periods. Unlike renewable energy sources that are dependent on weather conditions, coal power can be counted on to deliver electricity regardless of the time of day or year. This base-load power generation is crucial for meeting the fundamental energy needs of communities and industries.
Affordability and Accessibility
In many regions, coal remains arelatively affordable fuel source. This can translate to lower electricity prices for consumers and businesses. While the cost of renewable energy technologies has been declining rapidly in recent years, coal remains a competitive option in some areas, particularly where coal reserves are abundant and easily accessible. This affordability can be especially important for low-income communities and developing countries, where access to affordable energy is essential for economic development.
Contribution to a Diversified Energy Portfolio
Coal-fired power plants can also play a role in adiversified energy portfolio. By relying on a variety of energy sources, countries can reduce their dependence on any single fuel and improve their energy security. While phasing out coal is a crucial goal for addressing climate change, transitioning to a fully renewable energy system will require significant investments in infrastructure and technology. In the meantime, coal can provide a stable and reliable source of power while these transitions are underway. It is also important to note that advances in carbon capture and storage technologies, along with efficiency improvements in power plants themselves, continue to be pursued to mitigate carbon emissions.
How Coal is Used to Generate Electricity: Step-by-Step
The process of generating electricity from coal involves several key steps, each playing a crucial role in converting the stored energy in coal into usable electricity.
1. Coal Preparation and Handling
The first step is getting the coal ready for burning. This usually involvescrushing and grinding the coal into a fine powder. This increases the surface area of the coal, allowing it to burn more efficiently. The pulverized coal is then transported to the furnace. This initial step is crucial for ensuring efficient combustion and maximizing the energy output.
2. Combustion and Heat Generation
The pulverized coal is then blown into a large furnace where it isburned at high temperatures. The combustion process releases heat, which is used to boil water and create steam. The design of the furnace is critical for efficient combustion and minimizing emissions. Air pollution control systems are often integrated into the combustion process to remove pollutants such as sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides.
3. Steam Generation
The heat from the furnace is used toheat water in a boiler, generating high-pressure steam. The steam is then piped to a turbine. The boiler is a complex system of tubes that maximizes heat transfer from the hot gases to the water. The temperature and pressure of the steam are carefully controlled to optimize the efficiency of the turbine.
4. Turbine Operation
The high-pressure steam is directed onto the blades of aturbine, causing it to spin rapidly. The turbine is connected to a generator. The steam expands as it passes through the turbine, converting its thermal energy into mechanical energy. The design of the turbine blades is crucial for maximizing the efficiency of the energy conversion process.
5. Electricity Generation
Thespinning turbine drives a generator, which converts the mechanical energy into electrical energy. The generator consists of a rotating magnetic field that induces an electric current in a set of stationary coils. The electricity generated is then stepped up to a higher voltage for transmission across power lines.
6. Cooling and Condensation
After passing through the turbine, the steam iscooled and condensed back into water. This water is then recycled back to the boiler to repeat the process. Cooling towers or other cooling systems are used to dissipate the heat from the condensation process. Efficient cooling is essential for maintaining the overall efficiency of the power plant.
7. Emissions Control
Throughout the process, various emissions control technologies are used tominimize the release of pollutants into the atmosphere. These technologies may include scrubbers to remove sulfur dioxide, electrostatic precipitators to remove particulate matter, and selective catalytic reduction systems to reduce nitrogen oxides. Continuous monitoring systems are used to ensure that emissions levels comply with environmental regulations.
Tips Before Using Coal in a Power Plant
Before coal is even used in the plant, there are several crucial steps to consider to ensure safe, efficient, and environmentally responsible power generation.
Coal Quality Assessment: It's vital to thoroughly analyze the coal's composition. Knowing the sulfur content, ash content, and heating value allows for optimization of the combustion process and informs emission control strategies. Ignoring this could lead to inefficient burning and increased pollution.
Equipment Inspection: Regularly inspect and maintain all equipment, including the boiler, turbine, and generator. Faulty equipment can lead to shutdowns, safety hazards, and reduced efficiency.
Environmental Regulations: Be fully aware of and compliant with all environmental regulations regarding emissions and waste disposal. Failure to comply can result in hefty fines and legal repercussions. Ignoring emissions standards is simply not an option.
Common Issues and Solutions Related to Coal Power
Like any complex industrial process, coal power plants are subject to various operational challenges. Here are a few common issues and practical solutions: Slagging and Fouling: Ash deposits on boiler tubes can reduce heat transfer efficiency. Solution: Implement regular soot blowing and water washing to remove these deposits. Use coal with lower ash content, if feasible.
Equipment Failure: Turbine malfunctions and boiler tube leaks can disrupt operations. Solution: Implement a comprehensive preventative maintenance program. Use predictive maintenance techniques to identify potential issues before they become critical.
Emissions Exceedances: Failing to meet emissions standards can lead to penalties and plant shutdowns. Solution: Optimize combustion control to minimize pollutant formation. Invest in effective air pollution control equipment and ensure it is properly maintained.
Coal Supply Issues: Disruptions in coal delivery can threaten power generation. Solution: Maintain adequate coal stockpiles and diversify coal suppliers.
Conclusion
Generating electricity from coal is a multi-stage process involvingcombustion, steam generation, turbine operation, and electricity generation. While coal power continues to offerreliability and affordability, the need to mitigate its environmental impact is paramount. Ongoing efforts to improve efficiency, reduce emissions, and develop carbon capture technologies are essential for ensuring the future sustainability of coal power. In conclusion, understanding the entire process—from coal preparation to electricity transmission—provides valuable insights into the complexities and trade-offs associated with this important energy source. The future of energy includes innovation and a move toward sustainability for the global energy landscape.