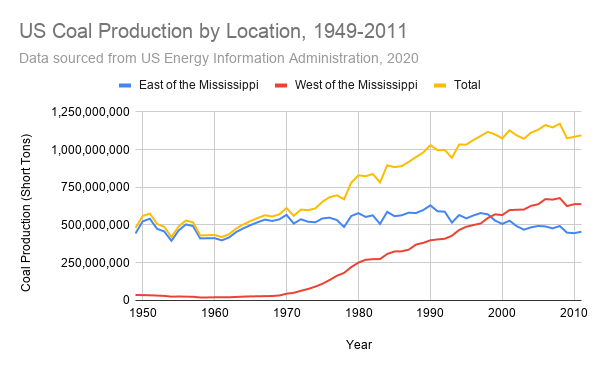
Is coal still a major player in America's energy landscape? Absolutely! Understanding the role of coal in our nation's power generation is crucial for informed discussions about energy policy and environmental impact. This post will delve into how much energy coal produces annually in the United States, exploring its historical significance, current contributions, and future trends in the face of evolving energy sources. We'll examine the numbers, discuss the benefits and drawbacks, and provide a clear picture of coal's place in the US energy mix.
All About Coal's Energy Production in the US
Coal has long been a workhorse of American energy production, fueling industries and powering homes for over a century. But how much energy are wereallytalking about each year? While the exact numbers fluctuate annually due to various economic and environmental factors, coal has historically contributed a significant portion of the total US electricity generation. The EIA (U.S. Energy Information Administration) is your best resource for themost accurate and up-to-datefigures.
In recent years, however, the percentage of electricity generated from coal has been steadily declining. This decline is primarily due to the rise of cheaper natural gas and the increasing adoption of renewable energy sources like solar and wind. Despite this decrease, coal still plays a noticeable role, especially in certain regions of the country. So, while theannual amount of energy produced by coalmight be decreasing, understanding the specific figures for each year provides essential insights into the shifting dynamics of the energy sector.
Coal's significance extends beyond just electricity generation. It's also used in industrial processes, such as steel production. While renewable energy sources are making great strides, coal's established infrastructure and large reserves have kept it in the mix. Therefore, accurately measuring and understanding its annual energy production is vital for informed energy policy and infrastructure planning.
Expert opinions on coal's future vary. Some believe it will continue to decline as cleaner energy options become more competitive. Others argue that coal can still play a role, particularly if carbon capture technologies become more widely adopted. Regardless of the projections, understanding the current energy output of coal is essential for comprehending the present state of US energy.
Benefits of Coal-Generated Energy
While coal faces increasing scrutiny due to its environmental impact, it still offers several benefits that have contributed to its long-standing role in US energy production. One primary advantage is itsabundanceandrelatively low cost. The United States has vast coal reserves, making it a domestically secure energy source and historically a reliable alternative to energy dependency on volatile global markets. This abundance has, in turn, kept electricity prices relatively stable and low compared to some other energy sources.
Another benefit is thereliabilityof coal-fired power plants. Unlike solar and wind, which are intermittent and dependent on weather conditions, coal plants can operate continuously, providing a stable and predictable supply of electricity. This reliability has been particularly valuable during periods of peak demand or when other energy sources are unavailable.
Historically, coal has also provided asignificant number of jobsin mining and power generation. These jobs have supported communities across the country, particularly in regions where coal mining is a major industry. While the number of coal-related jobs has declined in recent years, it remains a consideration in energy policy discussions.
Compared to other fossil fuels, coal power plants have a higher capacity factor. This translates into a higher utilization rate and greater efficiency in generating energy. Also, advancement in burning technology is starting to reduce the harm to the environment.
While the environmental concerns associated with coal are undeniable, its affordability, reliability, and job creation have been significant benefits that have sustained its presence in the US energy mix. However, with the rise of cleaner and more sustainable energy sources, these benefits are being weighed against the environmental costs, leading to a gradual shift away from coal in many parts of the country.
How to Understand Coal's Annual Energy Production Figures
Understanding the data on coal's energy production can seem daunting, but it's actually quite straightforward once you break it down. The U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) is the primary source for this information. They collect, analyze, and disseminate data on all aspects of energy, including coal. So, the first step is to head to the EIA website.
1. Accessing the EIA Data
Navigate to the EIA's coal data section. You'll find various reports, tables, and interactive tools. Look for the data series that covers electricity generation from coal. The EIA typically reports this data in units likemegawatt-hours (MWh)orgigawatt-hours (GWh)*. Make sure to select the annual data to get the total energy produced by coal in the US for a given year. The EIA also publishes a monthly energy review which is a collection of data about monthly U.S. energy usage.
Best practice is to download the data into a spreadsheet format (like CSV or Excel) for easier analysis.
2. Interpreting the Data
Once you have the data, pay attention to the units. One gigawatt-hour (GWh) is equal to 1,000 megawatt-hours (MWh). To put it in perspective, one GWh can power approximately 750 homes for a year. Also, look for any accompanying notes or explanations in the EIA report. The EIA often provides context and caveats about the data, such as changes in methodology or factors that may have influenced the results.
Common mistakes include misinterpreting the units or comparing data from different sources without accounting for potential differences in methodology. Always double-check the source and the units before drawing any conclusions.
3. Comparing to Other Energy Sources
To get a complete picture, compare coal's energy production to that of other energy sources like natural gas, nuclear, and renewables. The EIA also provides data on the total electricity generation from all sources, allowing you to calculate the percentage contribution of coal. This comparison will help you understand coal's relative importance in the overall energy mix.
Continue outlining further steps in a structured manner. Ensure each step is easy to follow.
Analyze the changes in coal's energy production over time. Look for trends and patterns. Has coal's contribution been increasing, decreasing, or staying relatively constant? Identifying these trends can provide valuable insights into the future of coal in the US energy sector.
Tips Before Analyzing Coal Energy Statistics
Before diving into the numbers on coal energy production, there are a few crucial things to keep in mind to ensure you're interpreting the data accurately and responsibly.
First,understand the context. Energy data doesn't exist in a vacuum. Various factors can influence coal production and consumption, including economic conditions, government regulations, technological advancements, and even weather patterns. Before you start crunching numbers, take some time to research the major events and trends that may have affected the energy sector in the year you're analyzing.
Second,be aware of the data limitations. Even the best data sources have limitations. The EIA's data is generally considered reliable, but it's based on surveys and estimates, which can have inherent uncertainties. Read the documentation carefully to understand the data's scope, methodology, and potential sources of error.
Third,avoid oversimplification. Energy is a complex issue, and there are often multiple perspectives and interpretations of the data. Avoid drawing simplistic conclusions or making sweeping generalizations based on a single data point. Consider the broader context and be open to different viewpoints.
Failing to consider the context, being unaware of data limitations, or oversimplifying the issue can lead to inaccurate or misleading conclusions. This can undermine your analysis and potentially contribute to misinformation.
Common Issues and Solutions Related to Interpreting Coal Energy Data
Even with the best preparation, you might encounter some common issues when working with coal energy data. Fortunately, there are solutions to help you navigate these challenges.
One frequent problem isdata inconsistenciesbetween different sources. For instance, data from the EIA might differ slightly from data published by other organizations. To address this, always prioritize data from reputable sources like the EIA. If you're comparing data from multiple sources, carefully examine the methodologies and definitions used to ensure they're compatible.
Another challenge isunderstanding the impact of policy changes. Government regulations, such as emissions standards or tax incentives, can significantly affect coal production and consumption. To address this, stay informed about relevant policy developments and consider how they might influence the data you're analyzing.
Finally,accounting for technological advancementscan be tricky. New technologies, like carbon capture and storage, could potentially change the economics and environmental impact of coal. Therefore, follow the technological advancement of the coal industry to take into account the environmental issues of this fossil fuel.
Conclusion
Understanding how much energy coal produces annually in the US is essential for grasping the complexities of our energy landscape. While coal's contribution has been declining, it remains a noteworthy player, particularly in specific regions and industrial applications. By exploring the historical significance, current benefits, and potential drawbacks, we can have informed conversations about energy policies.
Accurately interpreting coal production figures requires a comprehensive understanding of the data sources, units, and potential limitations. Additionally, knowing the preparation guidelines and the common issues that may arise during interpretation is key to successfully understanding the coal production figures. The U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) is a good resource for finding annual coal production figures.
By following these recommendations, we can promote more sustainable and informed energy practices in our daily lives.